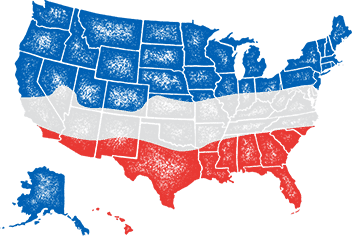
- When to plant:
- Spring, Fall
- Fertilizer:
- Varies
- Seeding rate:
- 40 lbs. per acre
- Overseeding rate:
- 1 lb. per 1,000 sq. ft.
- Seeding depth:
- 1/8 - 1/4 inch
- Ideal ph:
- 5.5 - 7.8
- Gmo:
- No
- Inoculant needed:
- H Type Inoculant - Lupine
- Coated or raw:
- Raw
- Lifecycle:
- Perennial
- Climate zones:
- Cool Season, Transition Zone, Warm Season
Perennial Lupine is a stunning flowering plant native to North America – this beautiful perennial species is known for its’ tall spikes of vibrant, pea-like flowers that grow in dense clusters atop upright stems. The beautiful flowers come in various shades of blue, purple, pink, and sometimes white, forming a visually striking display.
Product Information
- Botanic Name: Lupinus perennis
- Application or Use: Ornamental, Conservation, Habitat
- Germination Time: 10 - 14 days, under optimal conditions
- Growing Locations: Warm Season, Transition Zone, Cool Season
- Height: 3 - 4 feet
- Sunlight Requirements: 8+ hours, full sun for best results
- Advantages: Adapted to many soil types; showy blooms, excellent for landscaping; attracts pollinators.
- When to Plant: See instructions tab.
Product Information
These plants typically grow to be about 1 to 2 feet tall, though in optimal conditions, they can reach heights of up to 3 feet. They have a bushy growth habit and produce multiple flower spikes. Perennial Lupines bloom in late spring to early summer, showcasing their colorful flowers for several weeks. They are known for attracting bees and other pollinators.
The plant's foliage consists of palmate leaves with several leaflets that radiate from a central point on the stem. The leaves are typically a rich green color and add to the plant's overall appeal. Perennial Lupines prefer well-drained soil and thrive in full sun to partial shade. They are relatively drought-tolerant once established and are often found in meadows, prairies, and open woodland areas.
The flowers of Lupines are attractive to bees and butterflies, contributing to the garden's biodiversity. Perennial Lupines are popular in gardens and landscapes for their vibrant flowers. They work well in borders, cottage gardens, and naturalized areas, adding a splash of color.
Once established, Perennial Lupines are relatively low-maintenance. Regular deadheading can encourage prolonged flowering, and dividing plants every few years can help maintain vigor.
Perennial Lupines are treasured for their colorful and showy blooms, their attractiveness to pollinators, and their versatility in garden settings, making them a sought-after choice for adding vibrant colors to landscapes.
*Product packaging may appear different than what is pictured.
Wildflower Planting Time Based on Region:
Southeast
- Fall, Winter: Sowing wildflowers in Fall/Winter is the ideal time in the Southeast, with October 1 – December 31 being the best dates. The weather is ideal for starting seeds, and seedlings can grow and harden off before frost.
- Spring: A good time to plant wildflowers, especially annual species that flower quickly. Plant after the last frost date when soil temperatures have warmed to around 55°F, typically occurring within a month or so after the final frost of winter; this ensures the seeds can germinate properly without being affected by cold weather.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Southwest
- Fall: A good time to plant spring wildflowers in the desert Southwest. Fall's cooler temperatures and seasonal rains help seeds germinate. In the mountains, you can plant after spring frosts.
- Winter: In areas that get snow, winter seeding can give seeds an advantage in the spring.
- Spring: A popular time to plant wildflowers in most states. You can plant after the last frost and when the soil temperature is at least 55°F. In warmer climates, you can plant at the end of the rainy season.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Northeast
- Fall, Winter: The best time to plant wildflowers in the Northeast is in late fall, after the first frost but before heavy snow. This is known as dormant seeding and can take place from November to December. Cold temperatures and damp soil during the winter help wildflower seeds germinate.
- Spring: Plant in early spring, after the ground has thawed and soil temperatures reach around 55-65°F. This is a popular time to plant wildflowers because it's typically rainier, which helps water seedlings.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Midwest
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Western
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Pacific Northwest
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: In cooler zones with higher elevation, you can plant wildflowers in late spring to early summer, after the risk of frost has passed. You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
For best results, please review our Planting Guide and the specific product description before planting. Each product has recommended planting methods, timing, and seeding rates that are important for successful establishment. Following these guidelines will help ensure optimal performance and stand success.

Seed Quality
Hancock Seed is dedicated to delivering the best seeds possible to our customers. Hancock Seed grows and harvests many of our products, and we acquire the majority of the rest from other family farmers.
All these seeds are processed, packaged and shipped from Hancock Farm. This helps us ensure that our high standards are met. Unlike much of the competition, we refuse to sell you a seed that was not gathered during the last harvest. You will always receive fresh product from Hancock.
Every seed we grow comes with 40 years of experience behind it...you can rest assured that all of our products are cultivated in a method that assures its potential for growth.

Your cart ( 0 )

Perennial Lupine is a stunning flowering plant native to North America – this beautiful perennial species is known for its’ tall spikes of vibrant, pea-like flowers that grow in dense clusters atop upright stems. The beautiful flowers come in various shades of blue, purple, pink, and sometimes white, forming a visually striking display.
Product Information
- Botanic Name: Lupinus perennis
- Application or Use: Ornamental, Conservation, Habitat
- Germination Time: 10 - 14 days, under optimal conditions
- Growing Locations: Warm Season, Transition Zone, Cool Season
- Height: 3 - 4 feet
- Sunlight Requirements: 8+ hours, full sun for best results
- Advantages: Adapted to many soil types; showy blooms, excellent for landscaping; attracts pollinators.
- When to Plant: See instructions tab.
Product Information
These plants typically grow to be about 1 to 2 feet tall, though in optimal conditions, they can reach heights of up to 3 feet. They have a bushy growth habit and produce multiple flower spikes. Perennial Lupines bloom in late spring to early summer, showcasing their colorful flowers for several weeks. They are known for attracting bees and other pollinators.
The plant's foliage consists of palmate leaves with several leaflets that radiate from a central point on the stem. The leaves are typically a rich green color and add to the plant's overall appeal. Perennial Lupines prefer well-drained soil and thrive in full sun to partial shade. They are relatively drought-tolerant once established and are often found in meadows, prairies, and open woodland areas.
The flowers of Lupines are attractive to bees and butterflies, contributing to the garden's biodiversity. Perennial Lupines are popular in gardens and landscapes for their vibrant flowers. They work well in borders, cottage gardens, and naturalized areas, adding a splash of color.
Once established, Perennial Lupines are relatively low-maintenance. Regular deadheading can encourage prolonged flowering, and dividing plants every few years can help maintain vigor.
Perennial Lupines are treasured for their colorful and showy blooms, their attractiveness to pollinators, and their versatility in garden settings, making them a sought-after choice for adding vibrant colors to landscapes.
*Product packaging may appear different than what is pictured.
Wildflower Planting Time Based on Region:
Southeast
- Fall, Winter: Sowing wildflowers in Fall/Winter is the ideal time in the Southeast, with October 1 – December 31 being the best dates. The weather is ideal for starting seeds, and seedlings can grow and harden off before frost.
- Spring: A good time to plant wildflowers, especially annual species that flower quickly. Plant after the last frost date when soil temperatures have warmed to around 55°F, typically occurring within a month or so after the final frost of winter; this ensures the seeds can germinate properly without being affected by cold weather.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Southwest
- Fall: A good time to plant spring wildflowers in the desert Southwest. Fall's cooler temperatures and seasonal rains help seeds germinate. In the mountains, you can plant after spring frosts.
- Winter: In areas that get snow, winter seeding can give seeds an advantage in the spring.
- Spring: A popular time to plant wildflowers in most states. You can plant after the last frost and when the soil temperature is at least 55°F. In warmer climates, you can plant at the end of the rainy season.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Northeast
- Fall, Winter: The best time to plant wildflowers in the Northeast is in late fall, after the first frost but before heavy snow. This is known as dormant seeding and can take place from November to December. Cold temperatures and damp soil during the winter help wildflower seeds germinate.
- Spring: Plant in early spring, after the ground has thawed and soil temperatures reach around 55-65°F. This is a popular time to plant wildflowers because it's typically rainier, which helps water seedlings.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Midwest
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Western
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Pacific Northwest
- Fall, Winter: Plant in late fall (November–December) after the first frost. The seeds will overwinter and germinate in the spring. Fall planting is a good option for cooler climates and can give the seeds an early start in the spring.
- Spring: Plant in early spring (April–May) after the last frost when the soil temperature is consistently above 55°F. Spring is a popular time to plant because the soil is usually moist from rain, and you can see the wildflowers grow right away.
- Summer: In cooler zones with higher elevation, you can plant wildflowers in late spring to early summer, after the risk of frost has passed. You can plant wildflower seeds in the summer, but the hot sun can dry out the soil and stress your seedlings. Summer is a good time to plant quick-growing annual wildflowers.
Instructions
For best results, please review our Planting Guide and the specific product description before planting. Each product has recommended planting methods, timing, and seeding rates that are important for successful establishment. Following these guidelines will help ensure optimal performance and stand success.




















