- When to plant:
- Spring, Fall, Winter
- Fertilizer:
- Varies
- Seeding rate:
- 10 - 15 lbs. per acre
- Overseeding rate:
- 10 lbs. per acre
- Seeding depth:
- 1/4 inch
- Ideal ph:
- 5.5 - 7.0
- Gmo:
- No
- Inoculant needed:
- No
- Coated or raw:
- Coated
- Lifecycle:
- Semi-Perennial
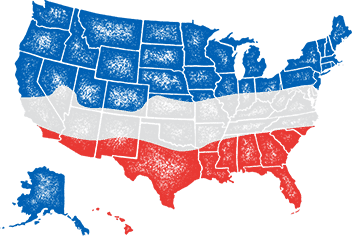
- Climate zones:
- Cool Season, Transition Zone, Warm Season
Berseem clover is a excellent cool season clover used for wildlife food plots, cattle forage and ground cover. Berseem clover is commonly planted with annual rye grass for livestock forage.
Product Information
- Application or Use: Cattle Forage, Livestock Grazing, Food Plot, Cover Crop, Erosion Control
- Germination Time: 5 - 7 days, under optimal conditions
- Growing Locations: Warm Season, Transition Zone, Cool Season
- Height: 1 - 3 feet
- Sunlight Requirements: 4+ hours
- Advantages: Superior quality, rapid fall growth, and winter hardiness.
- When to Plant: Recommended planting time is fall when night time temperatures are consistently below 65 degrees.
Product Description
- Fast winter growth rate
- Higher yielding than other winter clovers
- Produces forage until late May or early June
- Can grow as tall as 18 to 30 inches
-
Superior quality
Product Information
Berseem clover is a winter annual legume with oblong leaflets and hollow stems. It grows upright and produces yellowish-white flowers. Berseem Clover is selected for its superior quality, rapid fall growth, and winter hardiness.
Berseem clover is similar in drought tolerance to alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) but can tolerate more soil moisture than alfalfa or sweet clover (Melilotus alba L.). Although berseem clover grows on a variety of soils, a medium, loam soil that is slightly alkaline is best.
Production practices are much the same as for other winter annual legumes. If you grow seed for production and/or reseeding, allow the seed to mature in the spring and have the area fallowed with final seedbed preparation in late August. Include Boron when applying fertilizer.
*Product packaging may appear different than what is pictured.
Management and Use
Begin grazing or cutting berseem clover when the stand reaches 10 inches in height and when basal shoots begin to grow. Graze or clip to a 3-inch height to encourage new shoot production. It is critical to remove excess growth before temperatures reach the freezing mark. Heavy stand losses can occur from crown rot if excess forage is present during freezing.
For best results, rotate the grazing of berseem clover. This will give better total production by increasing yield and by increasing longevity of stand in the spring.
You can seed berseem clover in a mixture with crimson or white clover. In combination with perennial or annual cool-season grasses or cereals, high-quality forage is produced. It should greatly increase the quality of ryegrass for hay.
For best results, please review our Planting Guide and the specific product description before planting. Each product has recommended planting methods, timing, and seeding rates that are important for successful establishment. Following these guidelines will help ensure optimal performance and stand success.

Seed Quality
Hancock Seed is dedicated to delivering the best seeds possible to our customers. Hancock Seed grows and harvests many of our products, and we acquire the majority of the rest from other family farmers.
All these seeds are processed, packaged and shipped from Hancock Farm. This helps us ensure that our high standards are met. Unlike much of the competition, we refuse to sell you a seed that was not gathered during the last harvest. You will always receive fresh product from Hancock.
Every seed we grow comes with 40 years of experience behind it...you can rest assured that all of our products are cultivated in a method that assures its potential for growth.

Your cart ( 0 )

Berseem clover is a excellent cool season clover used for wildlife food plots, cattle forage and ground cover. Berseem clover is commonly planted with annual rye grass for livestock forage.
Product Information
- Application or Use: Cattle Forage, Livestock Grazing, Food Plot, Cover Crop, Erosion Control
- Germination Time: 5 - 7 days, under optimal conditions
- Growing Locations: Warm Season, Transition Zone, Cool Season
- Height: 1 - 3 feet
- Sunlight Requirements: 4+ hours
- Advantages: Superior quality, rapid fall growth, and winter hardiness.
- When to Plant: Recommended planting time is fall when night time temperatures are consistently below 65 degrees.
Product Description
- Fast winter growth rate
- Higher yielding than other winter clovers
- Produces forage until late May or early June
- Can grow as tall as 18 to 30 inches
-
Superior quality
Product Information
Berseem clover is a winter annual legume with oblong leaflets and hollow stems. It grows upright and produces yellowish-white flowers. Berseem Clover is selected for its superior quality, rapid fall growth, and winter hardiness.
Berseem clover is similar in drought tolerance to alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) but can tolerate more soil moisture than alfalfa or sweet clover (Melilotus alba L.). Although berseem clover grows on a variety of soils, a medium, loam soil that is slightly alkaline is best.
Production practices are much the same as for other winter annual legumes. If you grow seed for production and/or reseeding, allow the seed to mature in the spring and have the area fallowed with final seedbed preparation in late August. Include Boron when applying fertilizer.
*Product packaging may appear different than what is pictured.
Management and Use
Begin grazing or cutting berseem clover when the stand reaches 10 inches in height and when basal shoots begin to grow. Graze or clip to a 3-inch height to encourage new shoot production. It is critical to remove excess growth before temperatures reach the freezing mark. Heavy stand losses can occur from crown rot if excess forage is present during freezing.
For best results, rotate the grazing of berseem clover. This will give better total production by increasing yield and by increasing longevity of stand in the spring.
You can seed berseem clover in a mixture with crimson or white clover. In combination with perennial or annual cool-season grasses or cereals, high-quality forage is produced. It should greatly increase the quality of ryegrass for hay.
Instructions
For best results, please review our Planting Guide and the specific product description before planting. Each product has recommended planting methods, timing, and seeding rates that are important for successful establishment. Following these guidelines will help ensure optimal performance and stand success.


















